Author: Zhiyi Yuan, Nanyang Technological University
In this notebook, we create an open Dirac cavity as a hexagonal photonic crystal and analyze its spectrum and resonance properties.
from os.path import join
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tidy3d as td
from tidy3d import web
from tidy3d.plugins.resonance import ResonanceFinder
09:58:43 EST WARNING: Configuration found in legacy location '~/.tidy3d'. Consider running 'tidy3d config migrate'.
Create structure¶
a = 1.265
r = 0.272
t_slab = 0.2
n_side = 10
L = n_side - 0.5
Lx = 2*(L+2)*a
Ly = 2*(L*np.sqrt(3)/2+2)*a
x0, y0, z0 = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
medium_hole = td.Medium(permittivity=1.0) # holes (air)
medium_slab = td.Medium(permittivity=3.4**2) # slab
axis = 2
def open_dirac_cavity():
vertices = [
( L*a, 0.0),
( L*a/2, L*np.sqrt(3)*a/2),
(-L*a/2, L*np.sqrt(3)*a/2),
(-L*a, 0.0),
(-L*a/2, -L*np.sqrt(3)*a/2),
( L*a/2, -L*np.sqrt(3)*a/2),
]
slab_structure = td.Structure(
geometry=td.PolySlab(
slab_bounds=(z0 - t_slab/2, z0 + t_slab/2),
vertices=vertices,
),
medium=medium_slab,
name="slab_polyslab",
)
cylinders = []
for i in range(1, n_side + 1): # hexagon side length
center_x, center_y = x0 + (i - 1) * a, y0
for j in range(0, 6 - 5 * (i == 1)): # iterate through hexagon sides
for _ in range(0, i - 1 + (i == 1)): # iterate along each hexagon side
if i > 1:
center_x += a * np.cos(2*np.pi/3 + j*np.pi/3)
center_y += a * np.sin(2*np.pi/3 + j*np.pi/3)
cylinders.append(
td.Cylinder(
axis=axis,
radius=r,
center=(center_x, center_y, z0),
length=t_slab,
)
)
holes_structure = td.Structure(
geometry=td.GeometryGroup(geometries=cylinders),
medium=medium_hole,
name="holes_cylinders",
)
return [slab_structure, holes_structure]
structures = open_dirac_cavity()
slab = structures[0] # 显式赋值slab变量 - Explicitly assign slab variable
holes = structures[1] # 显式赋值holes变量 - Explicitly assign holes variable
#print(f"介质层结构:{structures[0].name}")
#print(f"孔阵列结构:{structures[1].name}")
print(f"holes number:{len(structures[1].geometry.geometries)}")
holes number:271
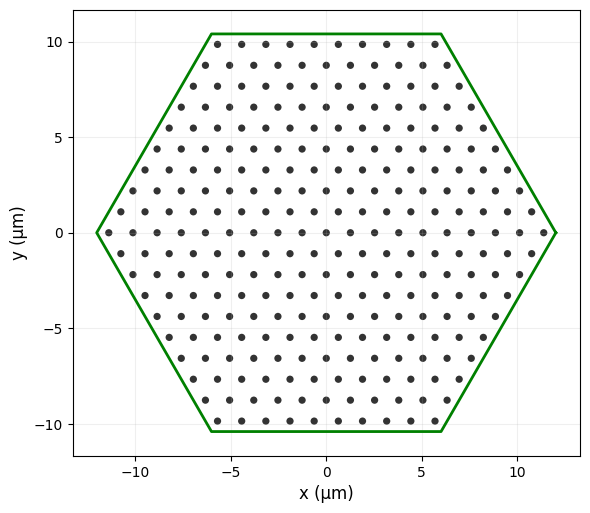
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
vertices = np.array(slab.geometry.vertices)
vertices_closed = np.vstack([vertices, vertices[0]]) # 闭合多边形 - Close the polygon
ax.plot(vertices_closed[:,0], vertices_closed[:,1], "g-", lw=2)
hole_centers_x = [] # 所有孔的x坐标 - x coordinates of all holes
hole_centers_y = [] # 所有孔的y坐标 - y coordinates of all holes
for cyl in holes.geometry.geometries:
center = cyl.center
hole_centers_x.append(center[0])
hole_centers_y.append(center[1])
ax.scatter(
hole_centers_x,
hole_centers_y,
s=cyl.radius * 100,
c="black",
marker="o",
edgecolors="none",
alpha=0.8,
)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
ax.set_xlabel("x (μm)", fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel("y (μm)", fontsize=12)
ax.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=10)
ax.grid(alpha=0.2)
x_min = vertices[:,0].min() - a
x_max = vertices[:,0].max() + a
y_min = vertices[:,1].min() - a
y_max = vertices[:,1].max() + a
ax.set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
ax.set_ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Create simulation¶
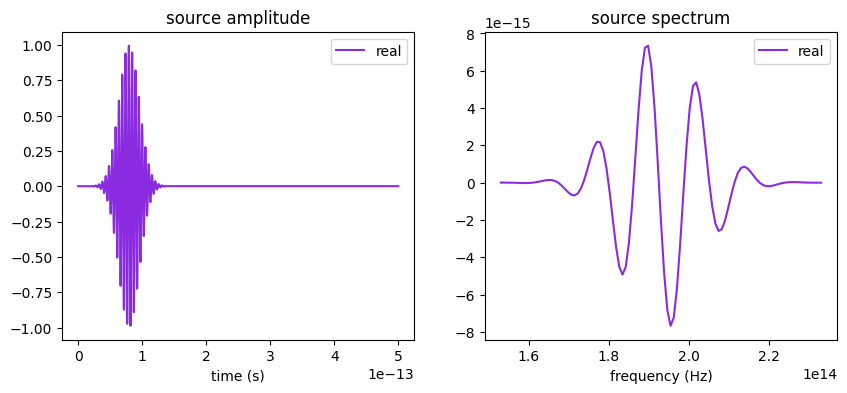
# Source frequency and width
freq0 = 192.5e12 # 200THz
fwidth = 10e12
runTime = 20e-12
# Source: plot time dependence to verify when the source pulse decayed
source = td.PointDipole(
center=(a/2-a/6, 0, 0),
source_time=td.GaussianPulse(freq0=freq0, fwidth=fwidth),
polarization="Hz",
)
sources = [source]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
source.source_time.plot(np.linspace(0, 5e-13, 2000), ax=ax[0])
source.source_time.plot_spectrum(times=np.linspace(0, 5e-13, 2000), ax=ax[1])
plt.show()
# Time series monitor for Q-factor computation
time_series = td.FieldTimeMonitor(
center=[a/2-a/6, 0, 0], size=[0, 0, 0], start=2e-13, name="time_series"
)
# near field
field_near = td.FieldMonitor(
center=[0, 0, 0],
size=[Lx, Ly, 0],
freqs = np.linspace(187.5e12, 197.5e12, 101),
name="field_near",
apodization=td.ApodizationSpec(start=3e-12, width=2e-13),
)
# far field fft
#ux = np.linspace(-1,1,101)
#uy = np.linspace(-1,1,101)
#field_far_fft = td.FieldProjectionKSpaceMonitor(
# center=(0, 0, t_slab/2 + 0.1),
# size=(Lx, Ly, 0),
# freqs = np.linspace(185e12, 200e12, 76),
# name="field_far_fft",
# proj_axis=2,
# ux=ux,
# uy=uy,
# apodization=td.ApodizationSpec(start=2e-13, width=2e-13),
#)
# Suppress warnings for some of the holes being too close to the PML
td.config.logging.level = "ERROR"
# Mesh step in x, y, z, in microns
steps_per_unit_length = 20
grid_spec = td.GridSpec(
grid_x=td.UniformGrid(dl=a / steps_per_unit_length),
grid_y=td.UniformGrid(dl=a / steps_per_unit_length * np.sqrt(3) / 2),
grid_z=td.AutoGrid(min_steps_per_wvl=steps_per_unit_length),
)
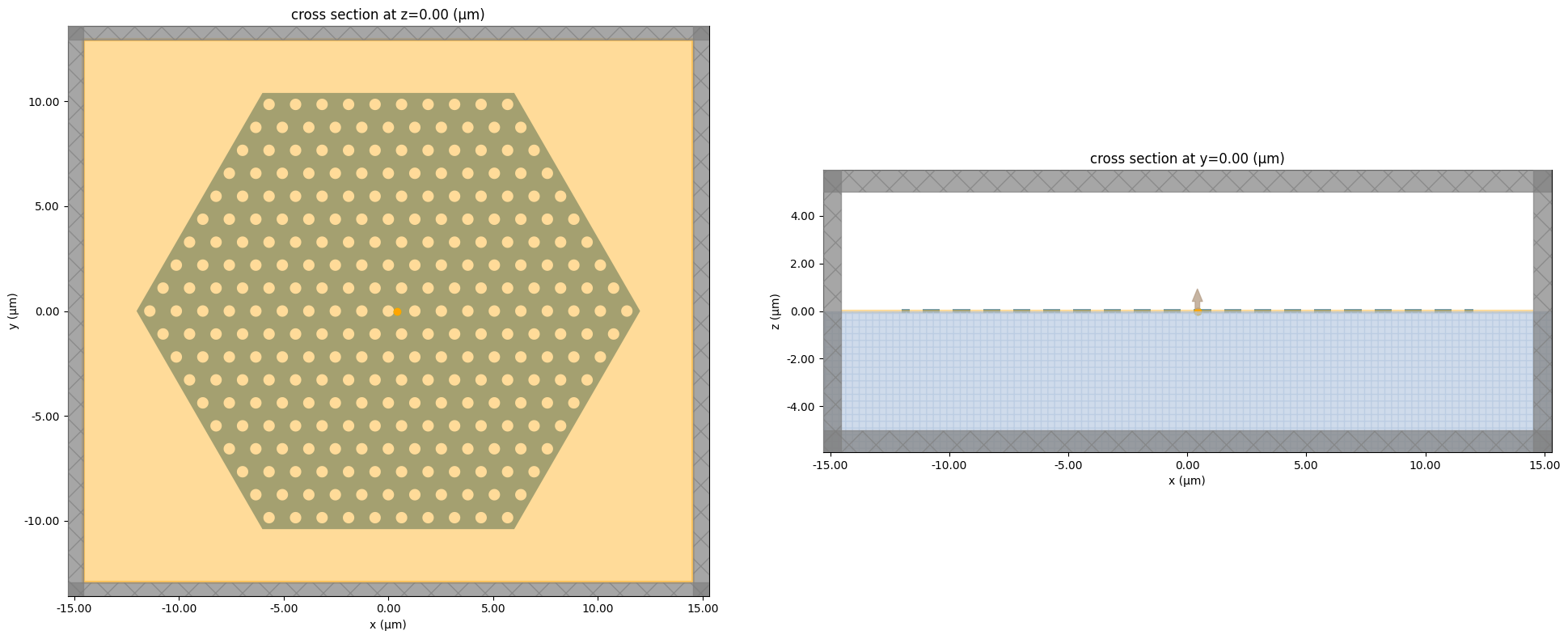
# Simulation
size_z = 10
sim_size = [Lx, Ly, size_z]
sim = td.Simulation(
size=sim_size,
grid_spec=grid_spec,
structures=structures,
sources=sources,
monitors=[time_series, field_near],
run_time=runTime,
boundary_spec=td.BoundarySpec.all_sides(boundary=td.PML()),
symmetry=(0, 0, 1),
shutoff=1e-5,
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 8))
sim.plot(z=0, ax=ax[0])
#sim.plot_grid(z=0, ax=ax[0], color="blue", alpha=0.3, linewidth=0.5)
ax[0].set_aspect("equal")
sim.plot(y=0, ax=ax[1])
ax[1].set_aspect("equal")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Run simulation¶
from tidy3d import web
# Create a job and upload it
job = web.Job(simulation=sim, task_name="Open_Dirac_Cavity", verbose=True)
# Estimate its maximum cost before running
estimated_cost = web.estimate_cost(job.task_id)
print(f"Estimated maximum cost: {estimated_cost:.3f} FlexCredits")
09:58:45 EST Created task 'Open_Dirac_Cavity' with resource_id 'fdve-678b6329-5709-489e-a4ca-a9957308305d' and task_type 'FDTD'.
View task using web UI at 'https://tidy3d.simulation.cloud/workbench?taskId=fdve-678b6329-570 9-489e-a4ca-a9957308305d'.
Task folder: 'default'.
Output()
09:58:47 EST Estimated FlexCredit cost: 2.095. Minimum cost depends on task execution details. Use 'web.real_cost(task_id)' to get the billed FlexCredit cost after a simulation run.
09:58:48 EST Estimated FlexCredit cost: 2.095. Minimum cost depends on task execution details. Use 'web.real_cost(task_id)' to get the billed FlexCredit cost after a simulation run.
Estimated maximum cost: 2.095 FlexCredits
sim_data = web.run(sim, task_name="Open_Dirac_Cavity", path="Dirac_Cavity_V2.hdf5",verbose=True)
Created task 'Open_Dirac_Cavity' with resource_id 'fdve-6ac4c5b0-515f-420e-9f31-209f45f33352' and task_type 'FDTD'.
View task using web UI at 'https://tidy3d.simulation.cloud/workbench?taskId=fdve-6ac4c5b0-515 f-420e-9f31-209f45f33352'.
Task folder: 'default'.
Output()
09:58:50 EST Estimated FlexCredit cost: 2.095. Minimum cost depends on task execution details. Use 'web.real_cost(task_id)' to get the billed FlexCredit cost after a simulation run.
09:58:51 EST status = queued
To cancel the simulation, use 'web.abort(task_id)' or 'web.delete(task_id)' or abort/delete the task in the web UI. Terminating the Python script will not stop the job running on the cloud.
Output()
09:58:59 EST starting up solver
running solver
Output()
10:00:12 EST early shutoff detected at 32%, exiting.
10:00:13 EST status = postprocess
Output()
10:00:35 EST status = success
10:00:37 EST View simulation result at 'https://tidy3d.simulation.cloud/workbench?taskId=fdve-6ac4c5b0-515 f-420e-9f31-209f45f33352'.
Output()
10:01:42 EST Loading simulation from Dirac_Cavity_V2.hdf5
Analyze spectrum¶
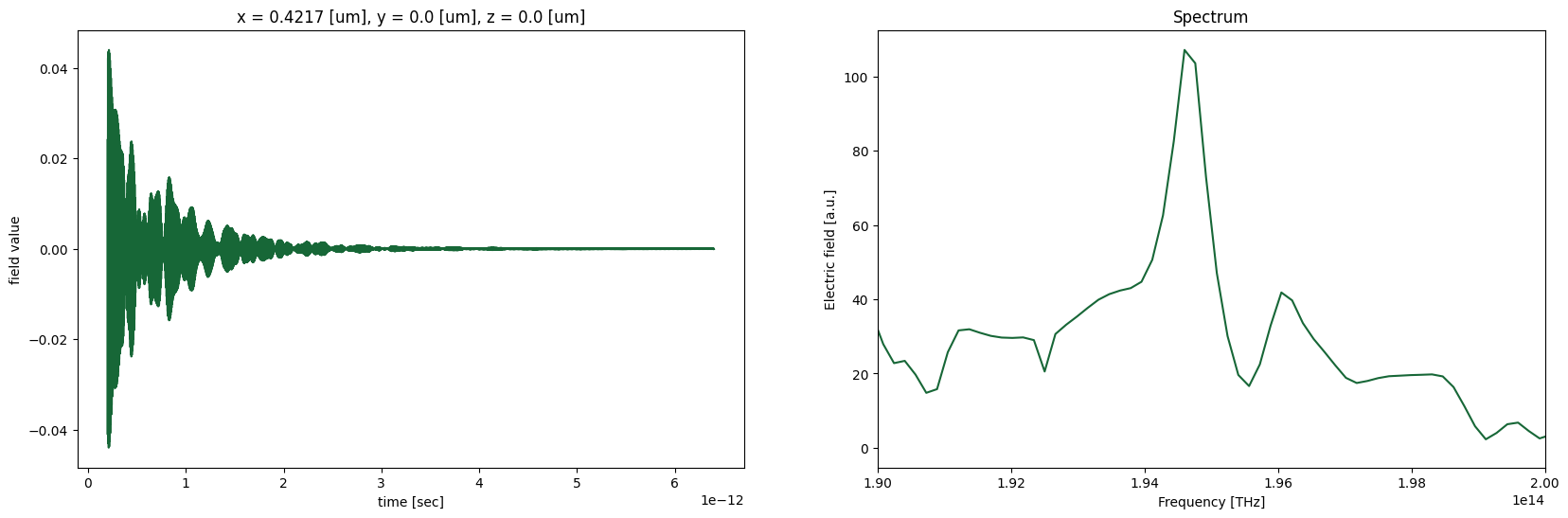
sim_data = td.SimulationData.from_file("Dirac_Cavity_V2.hdf5")
# Get data from the TimeMonitor
tdata = sim_data["time_series"]
time_series = tdata.Hz.squeeze()
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 6))
# Plot time dependence
time_series.plot(ax=ax1)
# Make frequency mesh and plot spectrum
dt = sim_data.simulation.dt
fmesh = np.linspace(-1 / dt / 2, 1 / dt / 2, time_series.size)
spectrum = np.fft.fftshift(np.fft.fft(time_series))
ax2.plot(fmesh, np.abs(spectrum))
ax2.set_xlim(190e12,200e12)
ax2.set_xlabel("Frequency [THz]")
ax2.set_ylabel("Electric field [a.u.]")
ax2.set_title("Spectrum")
plt.show()
Analyze resonance data¶
resonance_finder = ResonanceFinder(freq_window=(187.5e12, 195e12), init_num_freqs=100)
resonance_data = resonance_finder.run(sim_data["time_series"])
resonance_data.to_dataframe()
| decay | Q | amplitude | phase | error | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| freq | |||||
| 1.866466e+14 | 3.219630e+12 | 182.122663 | 0.244486 | -1.841334 | 0.000703 |
| 1.875533e+14 | 5.032551e+12 | 117.080987 | 0.391330 | 2.544543 | 0.001288 |
| 1.877141e+14 | 1.036471e+12 | 568.970173 | 0.016556 | 3.028083 | 0.000217 |
| 1.893997e+14 | 1.783065e+12 | 333.704424 | 0.202839 | 1.745468 | 0.000383 |
| 1.909463e+14 | 1.815567e+12 | 330.406590 | 0.336411 | 1.265731 | 0.000293 |
| 1.945941e+14 | 1.505145e+12 | 406.163921 | 0.240529 | -1.918391 | 0.000169 |
| 1.947196e+14 | 3.297701e+12 | 185.501860 | 0.130286 | 0.123704 | 0.001281 |
| 1.959386e+14 | 2.605625e+12 | 236.242390 | 0.125737 | -1.974891 | 0.000624 |
| 1.972617e+14 | 3.434281e+12 | 180.449943 | 0.104981 | 3.109832 | 0.001481 |
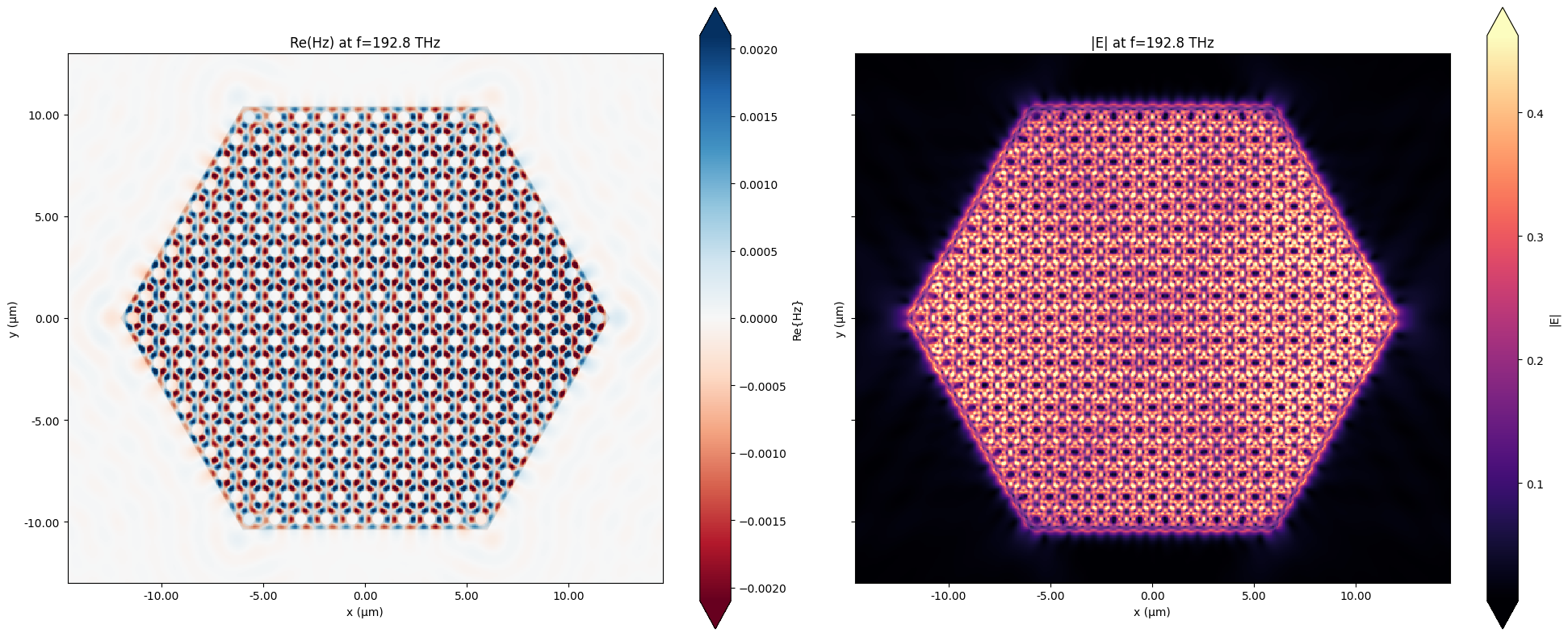
freq_hz = 192.8e12
freq_thz = freq_hz / 1e12
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 8), sharex=True, sharey=True)
sim_data.plot_field("field_near", "Hz", val="real", z=0, f=freq_hz, ax=ax1, eps_alpha=0.1)
ax1.set_title(f"Re(Hz) at f={freq_thz:.1f} THz")
sim_data.plot_field("field_near", "E", val="abs", z=0, f=freq_hz, ax=ax2, eps_alpha=0.1)
ax2.set_title(f"|E| at f={freq_thz:.1f} THz")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()